Asherman’s Syndrome is a condition that affects thousands of women worldwide, yet it remains underdiagnosed and often misunderstood. Characterized by the formation of scar tissue within the uterus, it can significantly impact menstruation and fertility. If you or a loved one are experiencing irregular periods or unexplained infertility, understanding Asherman’s Syndrome is the first step toward reclaiming your reproductive health.
In this guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Asherman’s Syndrome. You are not alone in this journey, and with the right information, you can take proactive steps toward recovery. Let’s navigate this condition together and empower you with knowledge and solutions.
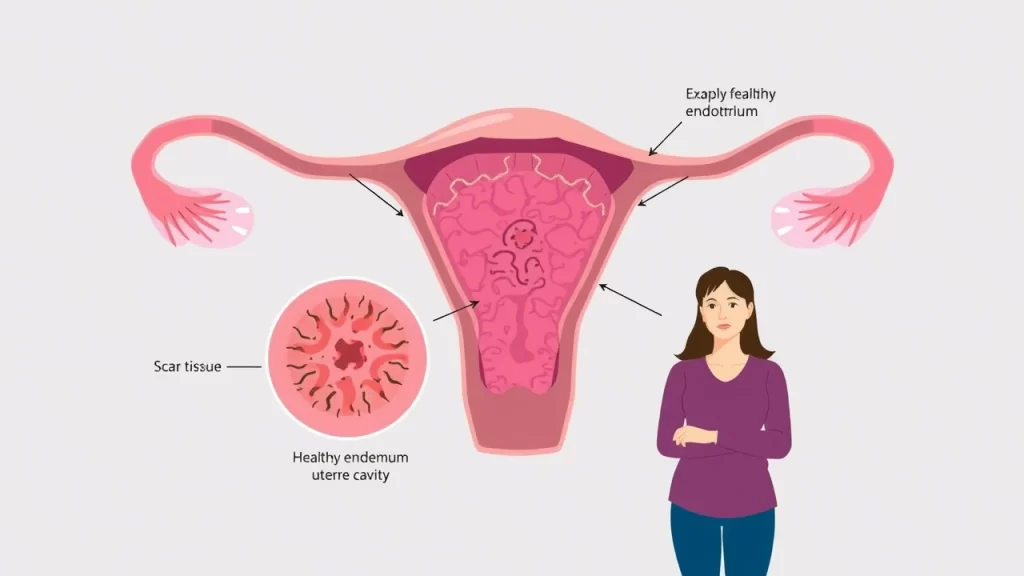
What Causes Asherman’s Syndrome?
Asherman’s Syndrome occurs when scar tissue forms inside the uterus, often as a result of uterine trauma. Common causes include:
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): A procedure frequently performed after miscarriage, abortion, or excessive bleeding.
- Cesarean Section or Uterine Surgery: Any surgical intervention on the uterus can lead to adhesions.
- Pelvic Infections: Chronic endometritis or untreated infections can contribute to scarring.
- Radiation Therapy: In rare cases, cancer treatments may damage uterine tissue.
Women who undergo multiple D&Cs or have had previous uterine surgeries are at a higher risk of developing Asherman’s Syndrome.
How Uterine Scarring Affects Menstruation
One of the earliest signs of Asherman’s Syndrome is a change in menstrual patterns. These changes may include:
- Lighter or Absent Periods (Hypomenorrhea or Amenorrhea): Scar tissue can block menstrual flow, leading to a noticeable decrease or absence of periods.
- Painful Menstruation (Dysmenorrhea): Some women experience cramping due to trapped menstrual blood.
- Difficulty Conceiving: If scarring obstructs implantation, achieving pregnancy can become challenging.
Recognizing these symptoms early can help with prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Link Between Asherman’s and Infertility
The presence of scar tissue inside the uterus can prevent pregnancy by:
- Blocking Sperm Passage: Adhesions may limit sperm movement, reducing fertilization chances.
- Preventing Implantation: A compromised endometrial lining makes it difficult for a fertilized egg to attach.
- Increasing Risk of Miscarriage: If implantation occurs in a scarred area, it may lead to pregnancy loss.
Women with Asherman’s Syndrome often require medical intervention to restore fertility.
Diagnosis: Detecting Uterine Adhesions Early
Diagnosing Asherman’s Syndrome involves several tests:
- Hysteroscopy: A thin camera inserted into the uterus provides a direct view of adhesions.
- Sonohysterography: A specialized ultrasound with saline infusion highlights abnormalities in the uterine cavity.
- MRI or Standard Ultrasound: While less precise, these imaging methods may detect severe scarring.
If you experience symptoms like absent periods or unexplained infertility, consult a specialist for an evaluation.
Asherman’s Syndrome – Treatment Options for Restoring Fertility
Treatment for Asherman’s Syndrome focuses on removing adhesions and promoting endometrial healing:
- Hysteroscopic Adhesiolysis: A minimally invasive procedure where a surgeon cuts and removes scar tissue.
- Estrogen Therapy: Often prescribed post-surgery to encourage endometrial regrowth.
- Balloon Stenting or IUD Placement: Used temporarily to prevent the walls of the uterus from re-adhering.
- Physical Therapy and Acupuncture: Some women find complementary treatments beneficial for uterine healing.
Early treatment significantly increases the chances of conceiving and maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
Preventing Asherman’s After Surgery
If you are undergoing a uterine procedure, consider these preventive steps:
- Request Gentle Surgical Techniques: Minimally invasive options reduce scarring risks.
- Take Prescribed Antibiotics: Preventing infection lowers the chance of adhesion formation.
- Use Estrogen Therapy: If recommended, this can support endometrial recovery.
- Follow Up with Regular Checkups: Early detection of adhesions ensures timely intervention.
Asherman’s Syndrome FAQs
What are the main causes of Asherman’s Syndrome?
The most common causes are repeated D&Cs, uterine surgeries, and untreated infections.
Can Asherman’s Syndrome be reversed?
Yes, hysteroscopic surgery effectively removes adhesions in most cases, restoring menstrual function and fertility.
Is pregnancy possible after Asherman’s Syndrome treatment?
Many women successfully conceive after treatment, though individual outcomes vary based on severity and response to therapy.
How can I prevent complications from Asherman’s Syndrome?
Regular medical follow-ups, adherence to treatment plans, and prompt action when symptoms appear can help manage the condition effectively.

Conclusion
Asherman’s Syndrome can be a challenging diagnosis, but with the right approach, fertility and menstrual health can often be restored. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—many women have successfully overcome Asherman’s and gone on to have healthy pregnancies.
If you suspect you have Asherman’s Syndrome, consult a healthcare provider to explore your treatment options. Share this article with someone who might find it helpful, and take the first step toward healing today!
Additional Resources:

