Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. This disorder causes the airways in the lungs to widen and become damaged, resulting in difficulty clearing mucus and increased susceptibility to infections. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and how to manage bronchiectasis effectively.
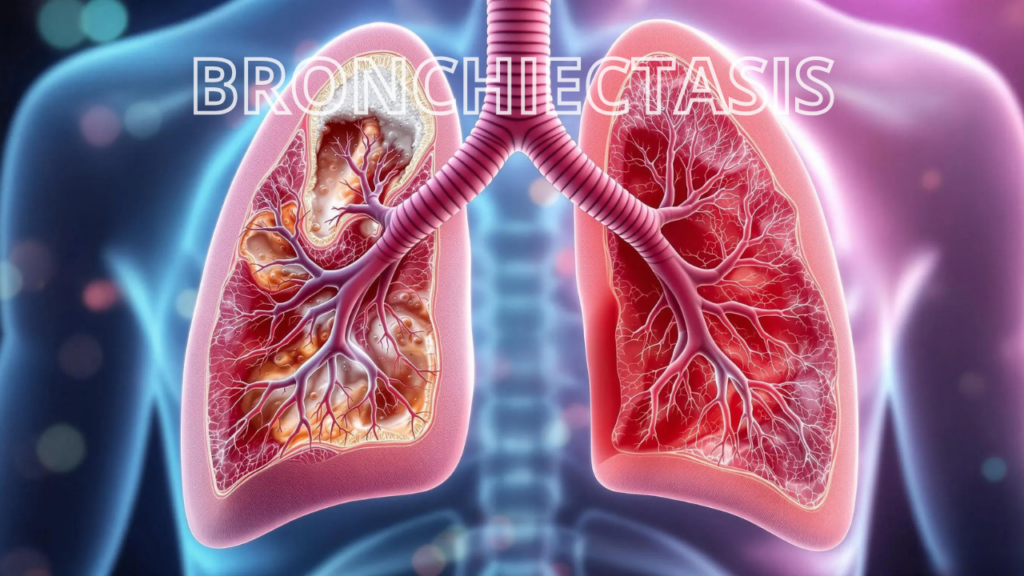
What is Bronchiectasis? An Overview
Bronchiectasis is a disease characterized by permanent dilation of the bronchi, the airways that carry air to the lungs. The condition leads to the weakening of the airway walls, causing mucus to accumulate, which in turn makes the lungs more prone to infections. Over time, this damage can result in a decrease in lung function, making breathing more difficult.
Bronchiectasis can affect anyone, though it is often diagnosed in those with a history of lung infections or chronic respiratory conditions. Though not as well-known as other lung diseases like asthma or COPD, bronchiectasis is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent long-term complications.
Common Causes of Bronchiectasis
There are several factors that can lead to the development of bronchiectasis. Some of the most common causes include:
- Chronic Respiratory Infections: Repeated infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, can cause irreversible damage to the airways. Infections that go untreated or are not adequately managed are a major risk factor.
- Cystic Fibrosis: This genetic disorder affects the production of mucus, leading to thickened mucus in the lungs, which promotes infections and results in bronchiectasis.
- Immune System Disorders: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or primary immunodeficiencies can impair the body’s ability to fight infections, increasing the risk of bronchiectasis.
- Aspiration: Inhalation of foreign substances like food or liquids into the lungs can cause inflammation and damage to the airway, leading to bronchiectasis.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to harmful toxins, such as cigarette smoke or pollution, can also contribute to the development of this lung condition.
Symptoms and Warning Signs to Look For
Recognizing the symptoms of bronchiectasis early can help prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Chronic Cough: A persistent cough that produces large amounts of mucus is one of the hallmark signs of bronchiectasis.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, particularly during physical activity, can occur as the disease progresses.
- Frequent Lung Infections: Individuals with bronchiectasis are more prone to respiratory infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis.
- Fatigue: The body’s constant fight against infection can cause general tiredness and fatigue.
- Wheezing and Chest Pain: Wheezing and occasional chest discomfort may also accompany bronchiectasis.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How Bronchiectasis Affects Lung Function
As bronchiectasis progresses, the lungs become less effective at clearing mucus. The thick mucus that accumulates in the airways can lead to chronic infections and inflammation. This impairs lung function, causing the following:
- Decreased Oxygen Supply: Damage to the airways affects the ability to exchange oxygen in the lungs, which can lead to low oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
- Breathing Difficulty: As the lung tissue becomes scarred, the elasticity of the lungs is reduced, making it harder to expand and contract properly.
- Increased Risk of Complications: Persistent lung infections can lead to further damage, making the condition more difficult to manage over time.
Treatment Options for Managing Bronchiectasis
Managing bronchiectasis typically involves a combination of treatments to help alleviate symptoms, improve lung function, and prevent complications. Common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: These are used to treat infections and prevent flare-ups. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed for long-term use to prevent chronic infections.
- Mucus-Removal Techniques: Chest physiotherapy, such as postural drainage and percussion, can help clear mucus from the lungs. Additionally, devices like a vibrating vest may be used to aid in this process.
- Bronchodilators and Steroids: Medications that open the airways (bronchodilators) and reduce inflammation (steroids) can help improve breathing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be considered to remove damaged sections of the lung.
- Oxygen Therapy: For patients with low oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen may be necessary to help improve lung function.
Living with Bronchiectasis: Tips and Strategies
Living with bronchiectasis can be challenging, but with proper management, individuals can lead an active life. Here are a few tips for managing bronchiectasis:
- Follow Treatment Plans: Adhering to prescribed medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes is essential for managing the condition effectively.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can help improve lung function and overall health.
- Avoid Infections: Get vaccinated for pneumococcus and the flu, and practice good hygiene to minimize the risk of infections.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A well-balanced diet can support your immune system and overall well-being.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of any changes in your symptoms and consult your healthcare provider if necessary.

Conclusion
Bronchiectasis is a chronic and often underdiagnosed lung condition that can have a significant impact on health and well-being. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can manage the condition and improve their quality of life. Public awareness, early diagnosis, and support are key to reducing the burden of bronchiectasis, and it’s important to stay informed and take proactive steps to mitigate its effects.
For more detailed information on managing lung health, check out this resource and this article on bronchiectasis. Stay informed and take action today!


Pingback: E. coli Infection: Causes, Symptoms, and Outbreak Prevention - stay healthy today