Discover a comprehensive overview of acne, including its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how to manage this common condition effectively with expert advice.
Introduction to Acne: A Global Skin Concern
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions affecting millions of people worldwide, particularly adolescents and young adults. While it’s often considered a temporary issue, acne can significantly impact one’s self-esteem and emotional well-being. Whether it manifests as pimples, blackheads, or cysts, acne can vary in severity. Understanding its causes, diagnosis, and available treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Acne: Contents and Overview
The contents of acne typically include clogged pores, bacteria, and excess oil production in the skin. These factors lead to the formation of various types of lesions. Acne lesions are primarily categorized into comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), inflammatory lesions (papules and pustules), and more severe cystic acne. Acne generally occurs on areas of the skin that contain a higher concentration of sebaceous (oil) glands, such as the face, back, chest, and shoulders.
An overview of acne involves understanding how its formation is influenced by hormonal changes, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions. By analyzing these factors, individuals can gain insight into how to treat and prevent the condition more effectively.
Causes of Acne: Understanding the Roots of the Condition
Acne can arise from several causes, which can vary for each individual. One of the most significant contributors is hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or when using birth control. These fluctuations increase the production of sebum, the oily substance that can clog pores.
Another cause is the overproduction of skin cells, which can mix with sebum and form blockages. Bacteria known as Propionibacterium acnes thrive in clogged pores, leading to inflammation and the formation of pustules or cysts. Stress, diet, and certain medications can also exacerbate acne symptoms, although research on dietary links is still ongoing.
Diagnosis of Acne: Seeking Professional Guidance
Diagnosing acne typically involves a consultation with a dermatologist who will assess the severity of the condition. A dermatologist may examine the skin, review the patient’s medical history, and inquire about possible lifestyle factors contributing to the acne. In some cases, further testing may be necessary to rule out underlying health conditions, especially if acne appears to be hormonally triggered.
During diagnosis, it is essential to determine whether acne is non-inflammatory (blackheads and whiteheads) or inflammatory (pimples, pustules, and cysts). This classification helps in selecting the most effective treatment approach.
Treatment Options for Acne: Finding the Right Solution
When it comes to acne treatment, several options are available, ranging from over-the-counter solutions to more intensive treatments prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Topical Treatments: For mild acne, topical treatments like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids can help clear blocked pores, reduce inflammation, and promote faster skin cell turnover.
- Oral Medications: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics or hormonal treatments (like birth control) can help regulate sebum production and reduce inflammation. For persistent or cystic acne, oral retinoids, such as isotretinoin, may be prescribed.
- Light and Laser Therapy: Some individuals opt for light or laser therapies that target the bacteria causing acne and reduce oil production, providing an alternative to traditional treatments.
It is important to consult a dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to the individual’s skin type and the severity of their acne.
Complications of Acne: When Acne Becomes a Concern
While acne itself is not life-threatening, it can lead to several complications if not properly managed. These include:
- Scarring: One of the most common complications of acne is the formation of scars. These can range from shallow, discolored marks to deep pitted scars, which may require professional treatment, such as laser therapy or chemical peels, to improve appearance.
- Psychological Impact: Acne, especially severe cases, can significantly affect a person’s self-esteem and mental health. Anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal are common among individuals with persistent acne.
- Infections: If acne lesions are picked or improperly treated, they can become infected, leading to more severe skin issues and additional scarring.
Practical Tips for Managing Acne
While professional treatments are essential, there are several steps individuals can take to manage acne at home. First, maintaining a consistent skincare routine is crucial. This includes gentle cleansing twice a day with a non-comedogenic cleanser, followed by appropriate topical treatments. Avoid touching the face or picking at acne lesions, as this can spread bacteria and worsen the condition.
Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle can support the skin’s overall health. For example, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep are all important factors in promoting clearer skin.
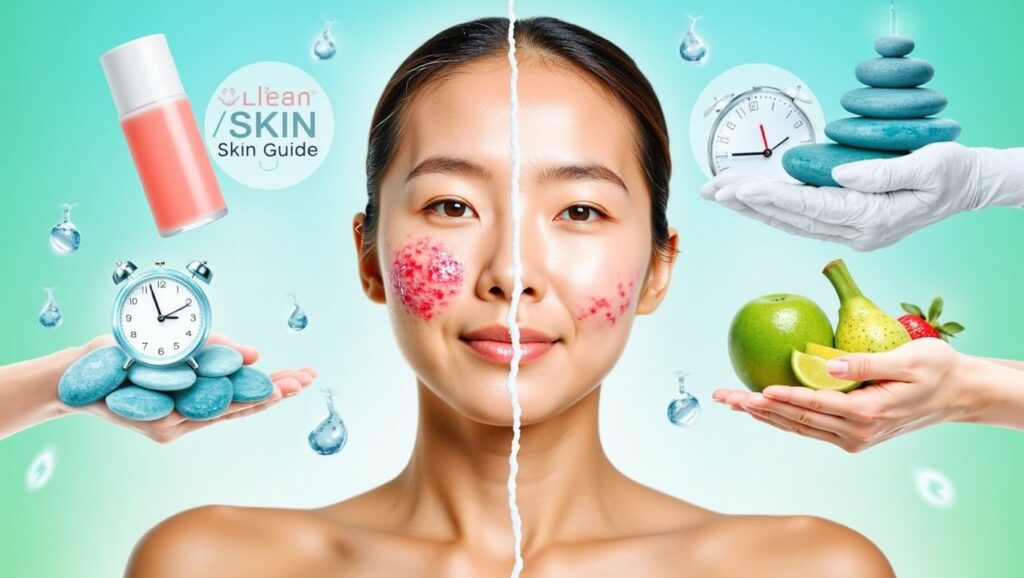

Conclusion: Stay Informed and Take Control
Acne, while common, can be effectively managed with the right knowledge and treatment plan. By understanding its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward clearer skin and improved self-confidence. Remember, acne is a treatable condition, and seeking professional guidance is key to finding the best solution for your skin.
By staying informed and consistent with your skincare routine, you can achieve lasting results. Whether mild or severe, acne is not something to suffer silently – effective treatments are available, and with the right approach, clear skin is within reach.
Natural Detoxification: Myths vs. Evidence-Based Practices


Pingback: HMPV Outbreak in China Raises Alarm Over Covid-Like Symptoms - stay healthy today